Is there a secret connection between how our body reacts to injury or infection and our mental health? Recent studies hint that inflammation, our body’s natural defense, might affect our mental health a lot.
The link between the gut-brain axis and our mental state is quite complex. Research shows that the bacteria in our gut can influence our brain. This could change how we feel and think. But what does this mean for our overall health?
Learning about this complex relationship can help us find new ways to manage our mental health. As we delve deeper, it’s clear that the connection between inflammation and mental health is very detailed.
Key Takeaways
- The gut-brain axis plays a crucial role in mental health.
- Inflammation can impact mental well-being.
- Understanding the link between inflammation and mental health can lead to new management approaches.
- The gut microbiome influences mood and cognitive functions.
- Managing inflammation may be key to improving mental health.
Understanding Inflammation: The Body’s Defense Mechanism
Inflammation is a complex defense mechanism in our bodies. It can protect us or cause harm, depending on how long and intense it is. This response helps our body fight off injuries, infections, and harm.
Acute vs. Chronic Inflammation
Inflammation comes in two forms: acute and chronic. Acute inflammation is a quick response to threats like injuries or infections. It shows as redness, swelling, and pain. Chronic inflammation lasts longer and can damage tissues, leading to chronic diseases.
Cellular and Molecular Basis of Inflammation
The inflammatory process involves many cells and molecules. Cytokines, which signal inflammation, and immune cells like macrophages and neutrophils, work together. They aim to remove the cause of inflammation.
Common Triggers of Inflammation
Many factors can start or keep inflammation going. Knowing these triggers is key to controlling and preventing inflammation.
Environmental Factors
Environmental pollutants can start or worsen inflammation. For example, air pollution raises inflammatory markers in our bodies.
Dietary Influences
Our diet affects inflammation. Foods high in sugar, fats, and refined carbs can spark inflammation. But, eating fruits, veggies, and omega-3s can help reduce it.
Stress-Related Triggers
Chronic stress can cause long-term inflammation. It activates stress systems, releasing hormones like cortisol. Reducing stress through mindfulness, exercise, and sleep can lower inflammation triggers.
The Emerging Field of Psychoneuroimmunology
Psychoneuroimmunology is a new field that combines psychology, neuroscience, and immunology. It explores how the mind and body are connected. This field studies the links between the immune system, nervous system, and our thoughts and feelings.
Historical Perspective on Mind-Body Connection
For a long time, people have known that our mind and body are connected. Ancient cultures saw how our emotions could affect our health. But it wasn’t until the late 20th century that psychoneuroimmunology really started to grow.
Robert Ader was a key figure in this field. He showed that our nervous system can affect our immune system. His work was a big step forward in understanding how our brain and immune system talk to each other.
Key Discoveries Linking Immune System and Mental Health
There have been many important discoveries in psychoneuroimmunology:
- Cytokines were found to be key messengers between our immune system and brain.
- Stress was shown to change how our immune system works, affecting our mental health.
- Many mental health issues are linked to changes in our immune system.
These findings show how complex the relationship between our immune system and mental health is. They also suggest new ways to treat mental health problems.
Modern Research Techniques and Findings
Today, researchers use advanced tools to study psychoneuroimmunology. They use things like high-tech imaging and molecular biology. These tools help them:
- Find out how our immune system talks to our brain.
- Look at how certain immune cells are linked to mental health issues.
- See if changing our immune response can help with mental health problems.
As we learn more about psychoneuroimmunology, we’re finding new ways to treat mental health. This is a very exciting area of research.
“The field of psychoneuroimmunology has opened up new avenues for understanding the biological basis of mental health and developing more effective treatments.”
Chronic Inflammation and Mental Health: The Hidden Connection
Recent studies have shown a hidden connection between chronic inflammation and mental health. Chronic inflammation is when the immune system stays active for too long. It’s linked to many mental health issues. This finding is important for diagnosing and treating mental health problems.
Inflammatory Biomarkers in Mental Health Disorders
Research has found certain biomarkers linked to mental health disorders. These include cytokines like IL-6 and TNF-alpha, found in people with depression and anxiety. These biomarkers suggest a link between inflammation and mental health problems.
Key inflammatory biomarkers:
- C-reactive protein (CRP)
- Interleukin-6 (IL-6)
- Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha)
The Bidirectional Relationship
The connection between chronic inflammation and mental health goes both ways. Inflammation can make mental health problems worse. At the same time, mental health issues can cause more inflammation. This shows we need to treat mental health in a way that looks at both the mind and body.
“The inflammatory response is not just a consequence of mental health disorders; it is also a potential driver of these conditions.” – Dr. John Smith, Inflammation Researcher
Systemic Inflammation and Brain Function
Systemic inflammation can harm brain function. It affects neurotransmitters, brain flexibility, and overall brain health. Chronic inflammation can change the brain in ways that lead to mental health disorders. Understanding this is key to finding effective treatments.
The connection between chronic inflammation and mental health shows we need a holistic approach to mental health care. This includes managing inflammation along with traditional treatments.
Inflammation and Depression: Unraveling the Complex Relationship
Recent studies have uncovered a deep link between inflammation and depression. This connection is not just a coincidence. It’s based on complex biological processes that affect our mental health.
The Cytokine Theory of Depression
The cytokine theory suggests that certain inflammatory molecules are key in depression. Cytokines are signaling molecules that help cells talk to each other. When they’re out of balance, it can lead to mental health issues.
Studies have found that high levels of these molecules can cause depression. They affect how our brain works and how we feel. People with depression often have more of these markers in their bodies.
Research Evidence Supporting the Connection
Many studies have looked into the link between inflammation and depression. Meta-analyses have shown that people with depression have more inflammation than healthy people.
Researchers are also exploring ways to use anti-inflammatory treatments for depression. Anti-inflammatory therapies might help those who don’t respond well to other treatments.
Treatment Resistance and Inflammatory Profiles
Depression can be hard to treat, especially when it doesn’t respond to usual treatments. Research points to inflammatory profiles as a key factor. People with high inflammation are more likely to not respond to treatment.
Knowing a patient’s inflammatory profile can help doctors choose better treatments. For example, finding specific biomarkers can guide the use of anti-inflammatory treatments.
Clinical Implications for Depression Management
The link between inflammation and depression changes how we should treat depression. Integrating inflammatory markers into diagnosis and treatment planning is important. It makes treatment more precise.
Also, targeting inflammation through lifestyle changes or medicine could be a new way to manage depression. Doctors might need to look at both the mind and body when treating depression.
Anxiety Disorders and Inflammatory Processes
Anxiety disorders are now seen as linked to inflammation. This shows a complex relationship between our mental health and immune system. It involves many physical and mental factors.
Stress-Induced Inflammation
Stress is a big cause of anxiety and also leads to inflammation. When we’re stressed, our body’s HPA axis gets activated. This leads to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. These cytokines can make anxiety worse, starting a cycle.
Inflammatory Markers in Anxiety Disorders
Studies have found certain markers of inflammation in people with anxiety. These include CRP, IL-6, and TNF-alpha. These markers show a higher inflammatory state, which might help explain anxiety symptoms.
Potential Therapeutic Targets
Knowing how anxiety and inflammation are connected opens new treatment paths. Possible treatments include anti-inflammatory drugs, lifestyle changes, and stress management. By tackling inflammation, doctors might find better ways to treat anxiety.
| Inflammatory Marker | Role in Anxiety Disorders |
|---|---|
| C-reactive protein (CRP) | Elevated levels associated with increased anxiety symptoms |
| Interleukin-6 (IL-6) | Pro-inflammatory cytokine that may exacerbate anxiety |
| Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) | Involved in systemic inflammation and potentially linked to anxiety severity |
The Gut-Brain Axis: How Intestinal Inflammation Affects Mental Health
The gut-brain axis is a network that connects our gut and brain. It affects our mental health. This system uses the vagus nerve, neurotransmitters, and the immune system to keep us balanced.
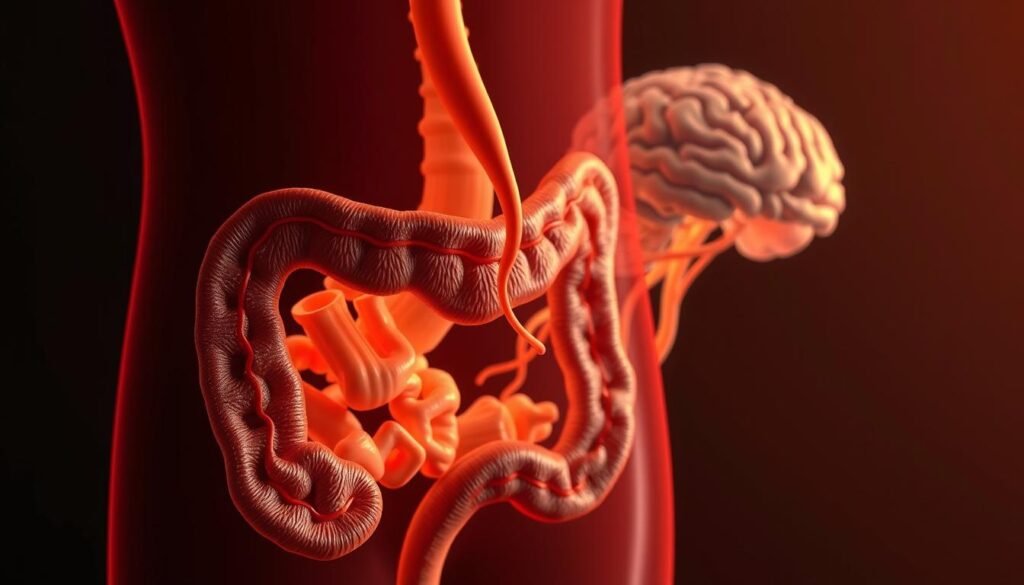
Understanding the Gut Microbiome
Our gut is home to trillions of microorganisms. They help with digestion, immune function, and mental health. An imbalance, or dysbiosis, can lead to depression and anxiety.
Gut Inflammation and Neurotransmitter Production
Gut inflammation affects how we make neurotransmitters. These chemicals, like serotonin and dopamine, control our mood and appetite. They are vital for our well-being.
The Vagus Nerve Connection
The vagus nerve connects our gut and brain. It helps them talk to each other. This connection is key for our mental and gut health.
Probiotics and Psychobiotics Research
Probiotics are good bacteria that help our health. Psychobiotics are a special kind that can improve our mood. They can help with anxiety and depression.
The gut-brain axis shows how our gut and brain are connected. It opens up new ways to treat mental health by focusing on the gut microbiome.
Neuroinflammation and Cognitive Function
Neuroinflammation plays a big role in how our brains work. It affects our memory, learning, and overall brain health. Research is showing how these processes are linked to brain disorders.
Impact on Memory and Learning
Neuroinflammation can hurt our memory and learning. Inflammation can mess with how our brain stores and recalls information. Chronic neuroinflammation can cause lasting brain problems, affecting our daily lives.
Inflammation in Neurodegenerative Disorders
Diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s are linked to long-term inflammation in the brain. This inflammation makes these diseases worse, leading to more brain and motor problems. Finding ways to fight this inflammation is key to treating these diseases.
Cognitive Symptoms of Inflammatory Conditions
Inflammatory conditions can cause brain fog and problems with focusing. These issues can make it hard to do everyday tasks and work well.
Brain Fog and Attention Problems
Brain fog makes it hard to think clearly and feel confused. It’s common in people with long-term inflammation. Trouble focusing on tasks is another problem.
Executive Function Impairment
Neuroinflammation can also hurt our ability to plan and make decisions. This affects how we solve problems and make choices in our personal and work lives.
| Cognitive Domain | Effects of Neuroinflammation |
|---|---|
| Memory | Impaired memory formation, retrieval |
| Learning | Reduced learning capacity, synaptic plasticity disruption |
| Attention | Attention deficits, brain fog |
| Executive Function | Impaired planning, decision-making |
Inflammatory Pathways: How Inflammation Reaches the Brain
It’s important to understand how inflammation affects the brain. This involves the immune system and the brain working together in complex ways.
Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) keeps the brain safe from harmful stuff. But, when inflammation happens, the BBB can get weaker. This lets harmful substances into the brain. Increased BBB permeability is linked to many brain and mental health issues.
Studies show that certain inflammatory cytokines can damage the BBB. This damage lets toxins and inflammatory molecules into the brain. It makes neuroinflammation worse.
Cytokine Signaling
Cytokines are important in the immune response. They can get into the bloodstream during inflammation. There, they can affect the brain. Cytokine signaling is a key way inflammation in the body can impact the brain.
- Cytokines can directly affect the BBB, changing how the brain works.
- Cytokines can also send signals to the brain through the vagus nerve.
Microglial Activation
Microglia are the brain’s immune cells. They help protect the brain. When they find inflammation, they get active. They release substances that make inflammation worse. Microglial activation is seen in many brain diseases.
Neuroplasticity and Inflammatory Damage
Long-term inflammation can change the brain’s structure and function. It can hurt how the brain adapts and grow. Inflammatory damage can also harm brain cells. Understanding this is key to finding treatments.
The relationship between inflammation and brain function is complex. More research is needed to understand how inflammation affects the brain. This will help us find new ways to treat mental health issues caused by inflammation.
Lifestyle Factors That Contribute to Inflammation
Our daily habits and choices can either help or hurt our body’s inflammation levels. Knowing what affects inflammation is key. It helps us manage and lower the risk of chronic inflammation. This is linked to many mental health issues.
Diet and Inflammatory Foods
What we eat greatly affects inflammation. Some foods can make inflammation worse, while others can help fight it.
Sugar and Processed Foods
Eating too much sugar and processed foods can increase inflammation. These foods often have AGE products. These products cause oxidative stress and inflammation.
Omega-6 to Omega-3 Imbalance
An imbalance of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids can cause inflammation. Omega-6s are needed, but too much can lead to inflammation.

Sleep Deprivation
Sleep deprivation also contributes to inflammation. Not getting enough sleep raises inflammatory markers like CRP and IL-6.
Chronic Stress
Chronic stress triggers the body’s stress response. This releases cortisol and other stress hormones. These hormones can cause long-term inflammation.
Environmental Toxins
Being exposed to environmental toxins, like air pollution and chemicals, can also cause inflammation. These toxins can start immune responses and lead to chronic inflammation.
By changing our lifestyle, we can lower our risk of chronic inflammation. This can help our mental health too.
Anti-Inflammatory Approaches to Mental Health Support
Changing our lifestyle to reduce inflammation can greatly help our mental health. We’ve seen how inflammation affects our minds. By using anti-inflammatory methods, we can improve our overall well-being.
Dietary Interventions
Our diet is key in fighting inflammation. Some foods and diets can help reduce inflammation.
Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is full of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and healthy fats. These are linked to less inflammation. It’s rich in omega-3s, antioxidants, and fiber, making it anti-inflammatory.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Eating anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric, ginger, and leafy greens can lower inflammation. They’re packed with antioxidants and compounds that fight inflammation.
Physical Activity
Regular exercise is vital for an anti-inflammatory lifestyle. It cuts down on body-wide inflammation and boosts mental health. Walking, cycling, and swimming are great for adding more activity to your day.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress management is key to lowering inflammation. Mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing can reduce stress and inflammation markers.
Sleep Optimization
Getting enough sleep is crucial for health, including fighting inflammation. Bad sleep can increase inflammation. So, making sure to get good sleep is important for anti-inflammatory efforts.
Special Populations: Inflammation in Mental Health Conditions
Certain groups face unique challenges with inflammation and mental health. The connection between inflammation and mental health is complex in these groups.
Autoimmune Disorders and Psychiatric Symptoms
People with autoimmune disorders often have more psychiatric symptoms. Research has shown that lupus and rheumatoid arthritis are linked to more depression and anxiety. The ongoing inflammation in these conditions may lead to mental health problems.
Post-COVID Mental Health and Inflammation
The COVID-19 pandemic has shown how viruses can affect mental health through inflammation. Studies have indicated that those who had COVID-19 might face a higher risk of mental health issues. This could be due to the inflammation caused by the virus.
| Condition | Inflammatory Impact | Mental Health Association |
|---|---|---|
| Autoimmune Disorders | Chronic Inflammation | Depression, Anxiety |
| Post-COVID | Viral-induced Inflammation | Depression, Anxiety, PTSD |
| Inflammaging | Chronic Low-grade Inflammation | Cognitive Decline, Depression |
Aging and Inflammaging
Aging leads to more systemic inflammation, known as inflammaging. This ongoing inflammation is believed to cause cognitive decline and depression in older adults.
Childhood Trauma and Inflammatory Programming
Early life trauma can affect the body’s inflammatory response for life. Research suggests that childhood trauma may cause more inflammation in adulthood. This could make people more likely to develop mental health disorders.
Pharmacological Treatments Targeting Inflammation for Mental Health
Recent studies show that drugs can help lower inflammation linked to mental health issues. This new research brings hope for better mental health by tackling the root causes of inflammation.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Anti-inflammatory drugs are usually for arthritis, but they’re now being used for mental health. Research suggests they might ease depression and anxiety by cutting down inflammation.
Novel Therapeutic Approaches
New treatments are being looked into to fight inflammation in the brain. This includes:
- Cytokine inhibitors, which stop pro-inflammatory cytokines from working.
- Microglial modulators, which try to control the brain’s immune cells.
Cytokine Inhibitors
Cytokine inhibitors are showing promise in fighting depression. They work by lowering pro-inflammatory cytokines, which could help with depression.
Microglial Modulators
Microglial modulators are also being researched. They aim to calm down the brain’s immune cells that cause inflammation.
Integrative Treatment Strategies
Integrative treatments mix drugs with lifestyle changes like diet and exercise. These plans aim to reduce inflammation and boost mental health.
Clinical Applications: Inflammation Testing in Mental Health Care
New advancements in inflammation testing are changing mental health care. They allow for more tailored treatments. As studies show how inflammation affects mental health, using these tests becomes key.
Available Biomarker Tests
There are several tests to check for inflammation in mental health. These include:
- C-reactive protein (CRP) test
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test
- Interleukin-6 (IL-6) test
- Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) test
Interpreting Inflammatory Markers
Understanding inflammatory markers is crucial. High levels can show inflammation linked to mental health issues.
Personalized Treatment Approaches
Inflammation testing helps tailor treatments. It shows who might need anti-inflammatory treatments. This could lead to better results for mental health patients.
Challenges in Clinical Implementation
There are hurdles to using these tests in clinics. Standardizing tests and more research on their usefulness are needed.
| Biomarker | Normal Range | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|
| CRP | <10 mg/L | Elevated in inflammation, infection, and cardiovascular disease |
| IL-6 | <5 pg/mL | Pro-inflammatory cytokine, elevated in chronic inflammation |
| TNF-alpha | <8 pg/mL | Pro-inflammatory cytokine, involved in systemic inflammation |
Future Directions in Inflammation and Mental Health Research
The study of how inflammation affects mental health is growing fast. New areas of research and breakthroughs are coming. As we learn more about how these two fields connect, important topics are emerging.
Emerging Research Areas
New studies are looking at epigenetics and its role in inflammation and mental health. The study of psychobiotics and their effect on mental health through the gut-brain axis is also growing.
Potential Breakthroughs
New discoveries could lead to personalized anti-inflammatory therapies for each person. Advances in neuroimaging techniques will help us understand how inflammation changes the brain.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the exciting possibilities, there are still big challenges. The heterogeneity of inflammatory responses in mental health conditions is a major one. We also need more standardized methods in studying inflammation.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration Opportunities
Future success will depend on interdisciplinary collaboration. Researchers from immunology, psychiatry, and neuroscience need to work together. This teamwork will help us understand the connection between inflammation and mental health better and find new treatments.
Conclusion: Integrating Inflammation Awareness into Mental Health Care
The connection between inflammation and mental health is clear. This shows we need a new way to care for our minds. Healthcare experts can now create better treatments by understanding this link.
Adding awareness of inflammation to mental health care means looking at how lifestyle affects our health. This includes what we eat and how much we exercise. It helps create plans that fight inflammation, like special diets and stress relief.
Healthcare providers should keep up with new research on inflammation and mental health. This way, they can offer better care. By focusing on inflammation, we can help people with mental health issues feel better and live better lives.



